137. GCD
Find the greatest common divisor (GCD) of n numbers.
Input. The first line contains the number of integers n (1 < n < 101). The second line contains n positive integers,
each not exceeding 30000.
Output. Print one number – the GCD of the given
numbers.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
2 15 25 |
5 |
SOLUTION
GCD
Algorithm
analysis
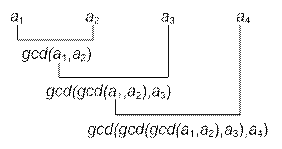
It is known that
GCD (a1,
a2, …, ai) = GCD (GCD (a1, a2, …, ai -
1) , ai)
Based on
this, the greatest common divisor of two, three, ..., n numbers can be
computed sequentially. For
example, for four numbers, the following equality holds:
GCD (a1,
a2, a3, a4)
= GCD (GCD (GCD (GCD (0, a1),
a2), a3), a4)
Algorithm
implementation
The function gcd computes the greatest common divisor.
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return (!b) ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
Read the input data and sequentially
compute
the GCD for the given n numbers, storing the result in the variable res.
res = 0;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n--)
{
scanf("%d", &b);
res = gcd(res, b);
}
Print the answer.
printf("%d\n", res);
Python implementation
import math
Read
the input data.
n = int(input())
lst = list(map(int,input().split()))
In the variable res, sequentially compute the GCD of the
given n numbers.
res = 0
for x in lst:
res = math.gcd(res, x)
Print the answer.
print(res)